Crete
 The island of Crete (Greek Kriti), which constitutes a region of Greece,
is oblong in shape, extending from east to west. Crete is mostly mountainous,
reaching a maximum elevation of 2,456 metres (8,058 feet) on Ida peak in
the range. Notable among the physical features of the island are a series
of flat upland basins and the large number of caves. The northern coast
of Crete has a number of good harbours, notably the Gulf of Soudha. The
southern coast, consisting largely of steep escarpments, is inaccessible
to shipping. The island is relatively well watered by numerous natural
springs and several rivers. Agriculture is the chief source of income in
Crete. Olives are the leading crop, while oranges, lemons, grapes, grain,
sheep, and goats are also raised. The only notable industries are food
processing and the manufacture of soap and textiles. The principal seaport
is Khania, but Iraklion is the capital and largest town. Modern archaeological
discoveries reveal that from about 3000 to 1200 BC Crete was the centre
of a flourishing Bronze Age civilization classified as the Aegean.
The island of Crete (Greek Kriti), which constitutes a region of Greece,
is oblong in shape, extending from east to west. Crete is mostly mountainous,
reaching a maximum elevation of 2,456 metres (8,058 feet) on Ida peak in
the range. Notable among the physical features of the island are a series
of flat upland basins and the large number of caves. The northern coast
of Crete has a number of good harbours, notably the Gulf of Soudha. The
southern coast, consisting largely of steep escarpments, is inaccessible
to shipping. The island is relatively well watered by numerous natural
springs and several rivers. Agriculture is the chief source of income in
Crete. Olives are the leading crop, while oranges, lemons, grapes, grain,
sheep, and goats are also raised. The only notable industries are food
processing and the manufacture of soap and textiles. The principal seaport
is Khania, but Iraklion is the capital and largest town. Modern archaeological
discoveries reveal that from about 3000 to 1200 BC Crete was the centre
of a flourishing Bronze Age civilization classified as the Aegean.
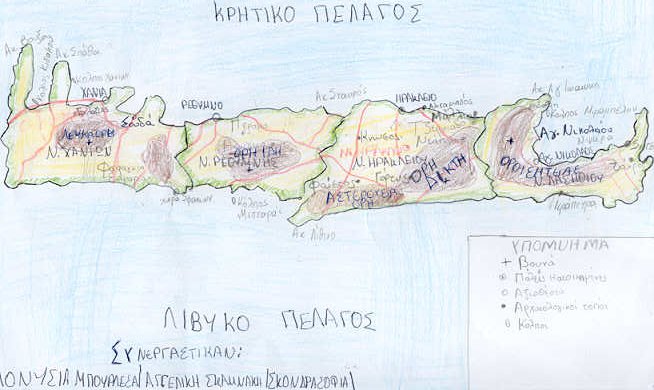
Map of Crete
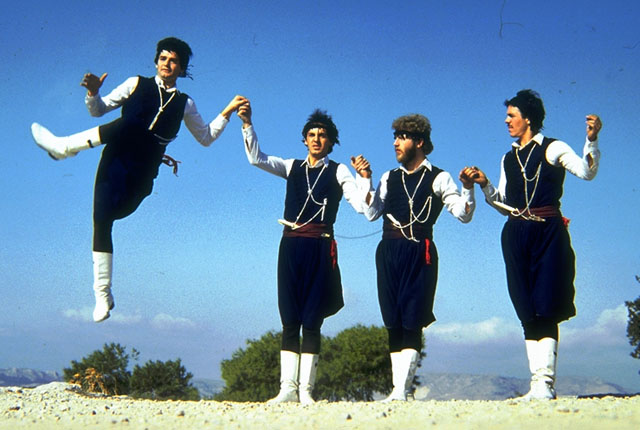

Traditional Cretan Dance
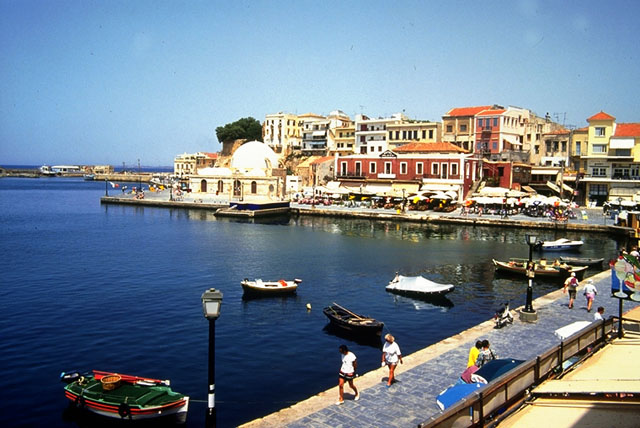

Chania
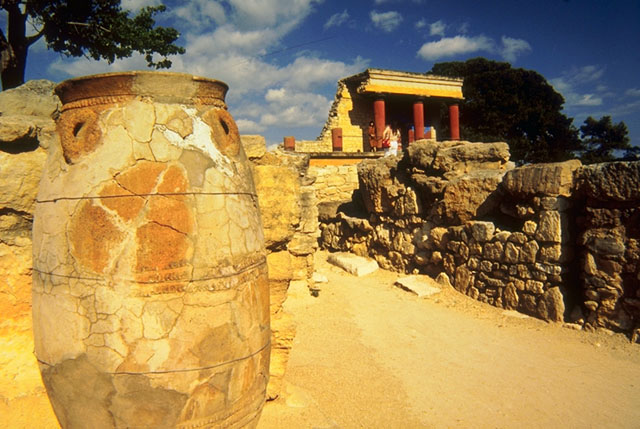

Knossos
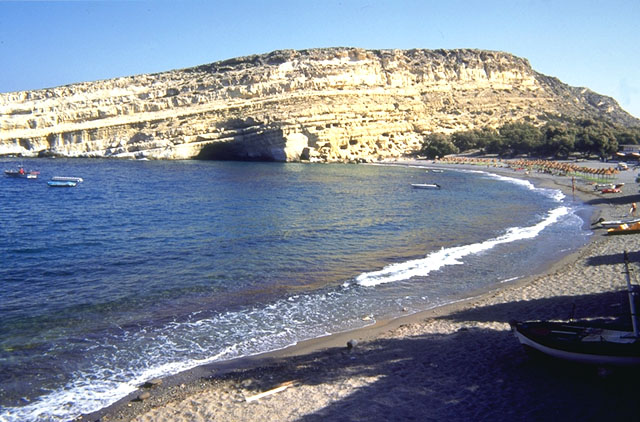

Matala







![]()